As the demand for safer, more efficient, and higher-performance batteries grows, two technologies often come into focus: semi-solid-state batteries and LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries. Both are being widely discussed in the consumer electronics and energy storage industries. But how do they actually compare? Let’s take a closer look.
1. Introduction: Why Compare These Two?
Batteries are the heart of every portable electronic device. Whether in power banks, electric vehicles, or renewable energy storage, the choice of battery chemistry directly determines safety, lifespan, capacity, and cost.
-
LiFePO4 has been proven in the market for over a decade and is trusted for its safety and durability.
-
Semi-solid-state batteries, on the other hand, represent the next stage of evolution, promising higher energy density and improved safety compared to traditional lithium-ion.
2. Understanding the Basics
Semi-Solid-State Battery
-
Uses a solid electrolyte mixed with gel or semi-liquid components, reducing the reliance on highly flammable organic liquid electrolytes.
-
Offers higher energy density than LiFePO4 and conventional lithium-ion.
-
Still in the stage of scaling up manufacturing and reducing costs.
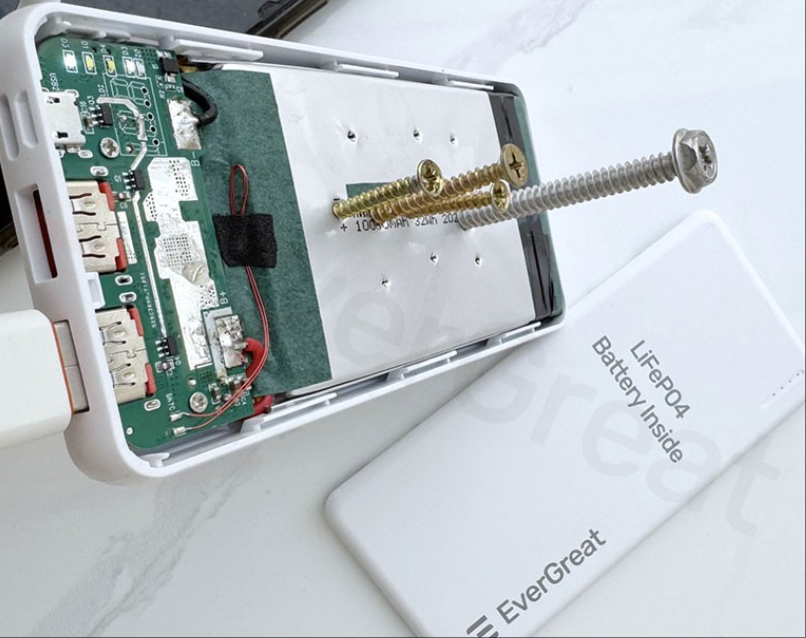
LiFePO4 Battery
-
Uses iron phosphate as the cathode material, which is chemically and thermally stable.
-
Known for excellent cycle life and very low risk of thermal runaway.
-
Lower energy density compared to semi-solid-state or NMC lithium batteries.

3. Safety Comparison
-
LiFePO4: Extremely stable, resistant to overcharging and high temperatures, making it a preferred choice in electric buses, home energy storage, and entry-level power banks.
-
Semi-Solid-State: Improved over traditional lithium-ion batteries since it reduces flammable liquid electrolytes. While safer than liquid-based lithium-ion, large-scale data on real-world safety performance is still being collected.
LiFePO4 currently wins in proven real-world safety, while semi-solid-state holds great potential for the future.
4. Energy Density & Performance
-
LiFePO4: Typically around 140–160 Wh/kg. This limits how compact a battery pack can be.
-
Semi-Solid-State: Can reach 250–300 Wh/kg in lab conditions, nearly double that of LiFePO4. This means smaller, lighter, and longer-lasting power banks for the same capacity.
Semi-solid-state is more promising for high-performance portable devices where compactness and weight matter.
5. Lifespan & Durability
-
LiFePO4: Can last 3000–5000 cycles, making it one of the longest-lasting battery chemistries.
-
Semi-Solid-State: Expected to improve cycle life, but current prototypes show performance between 1000–3000 cycles, depending on the manufacturer.
If long cycle life is the top priority, LiFePO4 still has the upper hand.
6. Cost & Manufacturing
-
LiFePO4: Mature technology with lower costs, supported by mass production in China and globally.
-
Semi-Solid-State: Still under development, with higher costs due to complex materials and less mature production lines.
LiFePO4 is more affordable for mass-market power banks today, while semi-solid-state batteries are better suited for premium or specialized products.
7. Applications in Power Banks & Consumer Electronics
-
LiFePO4: Suitable for large-capacity, cost-sensitive power banks where weight is less critical but long lifespan and safety are key.
-
Semi-Solid-State: Ideal for high-end, slim, and lightweight power banks, where portability and performance justify the higher cost.

8. Future Outlook
-
LiFePO4: Will remain dominant in storage, EV fleets, and mainstream power banks due to proven reliability and affordability.
-
Semi-Solid-State: Expected to expand as production costs fall, offering next-generation power solutions for compact electronics and premium markets.
9. Conclusion
Both LiFePO4 and semi-solid-state batteries have unique advantages:
-
If you need affordable, safe, and long-lasting power, LiFePO4 is the practical choice.
-
If you want cutting-edge, lightweight, high-energy solutions, semi-solid-state is the future.
For manufacturers, the smart approach may be to combine both technologies in different product lines, meeting diverse customer needs across markets.